The System menu can be displayed in two views. The basic settings are shown in the Normal View. This view is the default view when opening the menu. A complete overview of all settings is provided in the Advanced view.
Sections on this page:
•Name
•DNS
|
|
|
|
Clicking on the Advanced View button displays the advanced parameters. To collapse the extended display of the System menu item, click on the Normal View button in the advanced view.
In this menu, the most important parameters of the LAN connection of the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway are configured. The data entered here also serves as basic setting for numerous additional settings of the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway system.
The following sections describe the Advanced View since it also includes all settings of the Normal View.
Input fields for the description and/or identification of the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway. These parameters are used for example as the subject line in the automatic data backup as well as by SNMP. Otherwise, these are purely informative. The entries are freely selectable and each is optional.
Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|
Brief description of the system This is also displayed as the title in the browser and/or browser tab of the administration interface. |
|
Location of the system |
|
Proprietary ID of the system |
|
Contact person for the system |
|
Name of the system |
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
Parameters |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
(changed in 13.0.0) |
By default, this option is active. Definition of the network settings for the first LAN adapter (for example LAN1 and/or eth0 or also vic0 in virtual environments).
|
||
|
(for IPv4) |
Defines the IPv4 address of the respective interface. |
|
Deactivates IPv4. |
|||
By default, this option is active. The interface uses the IPv4 address to be specified in CIDR format. |
|||
The IPv4 address is obtained by DHCP.
|
|||
|
(for IPv6) |
Defines the IPv6 address of the respective interface. |
||
By default, this option is active. Deactivates IPv6. |
|||
The interface uses the IPv6 address to be specified in CIDR format. |
|||
The IPv6 address is obtained by DHCPv6.
|
|||
Creating an IPv6 address via autoconfiguration. |
|||
Connection speed of the interface. |
|||
Manually defining the type of Ethernet connection. |
|||
|
mediaopt full-duplex |
|||
|
mediaopt full-duplex |
|||
|
mediaopt full-duplex |
|||
Recommended setting. Automatic selection of the Ethernet connection based on the physical conditions (adapter used, cable, remote station). |
|||
Input of a package size that may deviate from the default ("maximum transmission unit" (MTU), see also https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maximum_transmission_unit) |
|||
|
2 - 4 (optional) |
By default, these options are inactive. An interface configuration is displayed for each physically existing network interface. Analogue to Interface 1 these are, for example Interface 2 - LAN2 and/or eth1 or also vic1 Interface 3 - LAN3 and/or eth2 or also vic2 Interface 4 - LAN4 and/or eth3 or also vic3 The detailed settings are identical to Interface 1. |
||
|
(optional) |
By default, this option is inactive. By using this setting, several interfaces can be bundled and used as a single logical unit. There are different procedures in this respect: |
||
For failure safety. Several switches can be used simultaneously. |
|||
For failure safety. Only one interface is active; in the event of a failure, the system switches to the next interface. Use of several switches possible. |
|||
Based on 802.3ad. Serves for load distribution and failure safety. Bundling of multiple interfaces to increase the possible bandwidths. Connection to only one switch with corresponding protocol support possible. |
|||
Used for load distribution. In the network, each remote peer is allocated an interface to be used. |
|||
Based on 802.3ad. Serves for load distribution and failure safety. Available interfaces are used alternately in the transmission direction; in the receiving direction, the maximum speed of a single interface can be used. |
|||
|
(optional) |
Enables local name resolution. A combination of IP addresses and host name/s must be entered for this.
Format: 62.2.145.228 update.seppmail.ch support.seppmail.ch 193.239.220.29 pool.ntp.org |
||
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
If several SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateways are operated in a cluster network (see also Clustering Multiple Systems etc seqq.), they can be addressed together via one or even several virtual IP addresses. The position of the individual machine in this network is defined by the priority (Priority).
|
|
Parameters |
Description |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
By default, these options are inactive. At this point, virtual IP addresses can be defined, which are usually used for cluster configurations (see also Clustering Multiple Systems et seqq.) (see Cluster). For this purpose, each alias requires 1.an IP address 2.the network mask 3.the VHID (Virtual Host Identification) 4.the interface to which the alias is to be bound 5.the priority of the interface in the network (primary, secondary, backup) to be specified.
|
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
(changed in 13.0.0)
The name of the system consists of the hostname and the domain, for example mycompany.tld.
These settings are the internal view, so they do not necessarily need to correspond to the data as it is valid from the Internet.
Parameters |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
The entries under Hostname and Domain are combined to form an FQDN, for example mycompany.tld. |
||
FQDN is obtained via DHCP. |
|||
FQDN is obtained via DHCPv6. |
|||
Input of the hostname of the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway, for example securemail |
|||
Input of the domain of the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway system, for example mycompany.tld. |
|||
|
|
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
Parameters |
Description |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Input of the gateway IP address via which all data packets are to be routed that are to be sent to destination addresses outside the local network segment.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(optional) |
If connections to networks which cannot be reached via the default gateway are to be established, the corresponding networks can be defined with their respective subnetwork under Destination and the corresponding Gateway. These static IP routes have priority over the use of the default router (default gateway). After saving a static route, a further input field is displayed.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(new in 13.0.0) |
The active routes are displayed separately in a table for IPv4 and IPv6.
|
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
Parameters |
Description |
||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Default setting. With this parameter, the system always attempts a DNS name resolution using the DNS root nameservers on the Internet. If this parameter has been selected, the resolution of DNS names may take a very long time, and the reaction of the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway can thus be delayed. Generally, this setting is to be selected if the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway sends data directly to the Internet, that is without an intermediate relay. |
|||||||||||||||||||
DNS queries for addresses for which the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway is not itself responsible are forwarded to superordinate DNS name servers. For this purpose, the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway should first route the DNS request to an internal DNS server in the proprietary network or the DNS servers of your Internet provider, which you can specify here. |
|||||||||||||||||||
By default, this option is inactive. Deactivates the prefilling of the DNS cache. This may cause names to take longer to resolve, but the result may be more up-to-date. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
(new in 13.0.8) |
By default, this option is set to "no". If set to "auto", the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway acts as DNSSec Client and a default anchor for the DNS root zone is used. The DNS resolver then validates DNSSEC signatures and e.g. stops the processing in case of failed validation. If set to "yes", the trust anchor must be manually configured. |
||||||||||||||||||
By default, this option is inactive. IPv6 responses from the DNS server are given preference. |
|||||||||||||||||||
Input of the first DNS server to which the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway is to forward DNS requests. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
(optional) |
If the primary DNS server is unavailable or does not respond, the DNS request is routed to the alternative DNS server entered here. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(optional) |
If neither the primary nor the first alternative DNS server are available, the DNS request is forwarded to the second alternative DNS server entered here. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(optional) |
Search list with domain names which are queried in the event of a DNS query one after the other. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(optional) |
Local zones are used when multiple forwarding and/or SMTP servers are to be addressed, but no local DNS server is available to resolve the required MX records. After saving, a further input field is displayed.
In the example entries below, the domain pseudo.local would be preferably resolved in mail1.pseudo.local with the IP address 10.0.0.11 since it has a preference level 10. If the server mail1.pseudo.local is not available, the entry with the preference 20, thus mail2.pseudo.local with the IP address 10.0.0.12 is used.
|
||||||||||||||||||
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
Is used for load distribution when a cluster is operated. This section is only visible if the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway is already part of a cluster.
Parameters |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
By default, these options are inactive. The SMTP load balancing only forwards emails to the entered cluster partners (see Distribute load to the following cluster members) once the defined simultaneous connections (see number of active connections before balancing) have been reached. |
||
At this point, the IP addresses of the cluster partners are entered for load balancing. The IP addresses are separated by a space in the input field.
|
|||
|
Definition of the number of simultaneous connections from which emails are to be forwarded to the registered cluster partners.This means that in the default setting (4), the fifth connection is forwarded to the first cluster partner entered under Distribute load to the following cluster members, the ninth connection is forwarded to the second cluster partner, and so on. |
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
(new in 14.0.0)
Offers two entries.
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The password for the technical support user has to be entered here. This only affects the console password, not the one for the Admin GUI. (Note that the console uses the Swiss keyboard layout.) |
A custom watchdog sender address could be entered here. In case of an empty value, 'watchdog@labnode1' is used as the watchdog sender mail address. |
Defines the settings for accessing the administration interface.
Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
This option is inactive by default and pre-set to 8080. Allows unencrypted access to the configuration interface via the HTTP protocol. |
By default, this option is active and set to the value 8443. Allows encrypted access to the configuration interface via the HTTPS protocol. The certificate used for access can be seen under SSL. |
|
By default, this option is set to the value 1800. Time in seconds until the automatic logout from the configuration interface due to inactivity. After an automatic logout, the last opened configuration menu is displayed when logging in again. |
|
|
By specifying the IP address of a specific network interface (see IP addresses Interface <n>), access to the administration interface can be restricted to this/these network interface(s). Multiple addresses can be entered by separating them with spaces. If, additionally, the SMTP traffic is to be bound to another interface (see Mail System SMTP Settings SMTP bind address), a clean separation of the administrative and user data traffic (emails) is thus achieved (keyword: administration network). |
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
(new in 12.1)
Defines the settings for API access (see also API Functions and/or https://docs.seppmail.com/api/) to the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway.
Parameters |
Description |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
By default, this option is inactive. Enables API access via the HTTPS protocol on the specified port (8445 by default). |
||||||
|
(changed in 13.0.0) |
||||||
|
If no configuration has been made yet, this is the first and only display. Otherwise, this field is below the accesses that have already been set up. |
|||||
|
By default, this option is active. Activates the access to be generated automatically after creation. |
|||||
By default, this input field is empty. A meaningful name for the access to be set up should be entered here. Via the trash button |
||||||
By default, this input field is empty. A token can be created via Generate further down in the section. Alternatively, a character string can also be entered here. |
||||||
By default, this input field is empty. The generation of an API token via Generate also generates an API secret. Alternatively, a character string can also be entered here. Via the eye button |
||||||
In the subsections of this option, the access authorisations for the access to be created are assigned. |
||||||
|
Selection menu for authorisation to individual Via the Get button |
|||||
|
a search function for the available permissions is available via the input field. |
|||||
by means of select all and/or unselect all, all permissions can be activated or deactivated simultaneously. |
||||||
see SEPPmail API crypto (used to read out key material)
|
||||||
|
Crypto / MPKI |
see SEPPmail API crypto (used to read out MPKI settings)
|
|||||
see SEPPmail API customer (used to read out customer (tenant) information)
|
||||||
For internal use! |
||||||
For internal use! |
||||||
For internal use! |
||||||
see SEPPmail API group (used to read out groups information)
|
||||||
For internal use! see SEPPmail API mail processing
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system (used to read out information of managed email domains) |
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system (used to read out groups information regarding email domains)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system (used to read out basic settings)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system (used to read out TLS settings of target systems)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system (used to read out email and disclaimer templates)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API statistics (used to read out statistics)
|
||||||
|
Users |
see SEPPmail API user (used to read out internal users and their key material)
|
|||||
see SEPPmail API webmail (used to read out GINA users)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API webmail (used to read out GINA domains). |
||||||
see SEPPmail API webmail (used to read out basic GINA settings)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API info (used to read out possible encryption methods for communication targets)
(see also X.509 Certificates, OpenPGP Public Keys, Domain Certificates and GINA accounts) |
||||||
Selection menu for authorisation to individual Via |
||||||
a search function for the available permissions is available via the input field. |
||||||
by means of select all and/or unselect all, all permissions can be activated or deactivated simultaneously. |
||||||
see SEPPmail API authenticate (is used to check possible REST accesses)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API crypto (used to define key material)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API customer (used to define customer (tenant) information)
|
||||||
For internal use! |
||||||
|
Filter / Config |
For internal use! |
|||||
For internal use! |
||||||
see SEPPmail API group (used to define groups information)
|
||||||
For internal use! see SEPPmail API mail processing
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system (used to create managed email domains) |
||||||
For internal use!
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system (used to define basic settings)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system (used to define TLS settings of target systems)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system / template (used to create email and disclaimer templates)
as well as SEPPmail API mail system / disclaimer
|
||||||
|
Tools / LDIF import |
For internal use! see SEPPmail API tools |
|||||
|
Users |
see SEPPmail API user (used to create internal users and supply them with key material)
|
|||||
see SEPPmail API webmail (used to create GINA users)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API webmail (used to create GINA domains). |
||||||
Selection menu for authorisation to individual Via |
||||||
a search function for the available permissions is available via the input field. |
||||||
by means of select all and/or unselect all, all permissions can be activated or deactivated simultaneously. |
||||||
see SEPPmail API crypto (used to customise key material)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API customer (used to customise customer (tenant) information)
|
||||||
For internal use! |
||||||
|
Filter / Config |
For internal use! |
|||||
For internal use! |
||||||
see SEPPmail API group (used to customise the groups information)
|
||||||
For internal use! see SEPPmail API mail processing
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system / managed domain (used to customise information of managed email domains) |
||||||
For internal use!
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system (used to customise basic settings)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system (used to customise TLS settings of target systems)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system / template (used to customise email and disclaimer templates)
as well as SEPPmail API mail system / disclaimer
|
||||||
|
Users |
see SEPPmail API user (used to customise the internal users and their key material)
|
|||||
see SEPPmail API webmail (used to customise the GINA users)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API webmail (used to customise the GINA domains).
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API webmail (used to customise GINA settings)
|
||||||
Selection menu for authorisation to individual Via |
||||||
|
a search function for the available permissions is available via the input field. |
|||||
by means of select all and/or unselect all, all permissions can be activated or deactivated simultaneously. |
||||||
see SEPPmail API crypto (used to remove key material)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API customer (used to remove customer (tenant) information) |
||||||
For internal use! |
||||||
|
Filter / Config |
For internal use! |
|||||
For internal use! |
||||||
see SEPPmail API group (used to remove groups information)
|
||||||
For internal use! see SEPPmail API mail processing
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system / managed domain (used to remove information of managed email domains)
|
||||||
For internal use!
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system (used to remove basic settings)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system (used to remove TLS settings of target systems)
|
||||||
see SEPPmail API mail system / template (used to remove email and disclaimer templates)
as well as SEPPmail API mail system / disclaimer |
||||||
see SEPPmail API user (used to remove the internal users and their key material) |
||||||
see SEPPmail API webmail (used to remove GINA users) |
||||||
see SEPPmail API webmail (used to remove GINA domains).
|
||||||
If the option is activated, a token with access to all existing and future tenants is generated. The option Assigned tenants remains greyed out. |
Visible only with activated client capability (see Customers). |
|||||
In the selection menu... |
||||||
|
a search function for the available tenants is available via the input field. |
|||||
by means of select all all available tenants can be selected simultaneously. |
||||||
The tenant "Default Customer" ([default], see Customers) is available in every client-capable system |
||||||
There is a separate checkbox for each tenant created |
||||||
|
Clicking on Generate generates an API token and an associated API secret. Via the button Add the access is saved. |
|||||
If access data have already been set up, they are displayed as created: |
||||||
By default, this option has the status set when it was created. Activates/deactivates the respective access. |
||||||
The Display name of existing accesses cannot be changed. |
||||||
The API token of existing accesses cannot be changed. Via the copy button |
||||||
The API secret can be changed if necessary. Via the eye button the copy button the refresh button |
||||||
In the subsections of this option, the access permissions for the respective access can be adjusted. The description of the subsections is identical to that of New API Token Access above and is therefore not listed here again. |
||||||
|
(new in 13.0.0)
If a user is authenticated via the end point "/auth", this is also displayed here. |
||||||
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
Defines the settings for accessing the GINA portal.
Parameters |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
This option is inactive by default and pre-set to 80. Enables unencrypted access to the webmail interface of the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway (GINA) via the HTTP protocol.
|
|||
By default, this option is active and set to the value 443. Enables encrypted access to the webmail interface of the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway (GINA) via the HTTPS protocol.
If the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway does not accept HTTPS requests directly from the Internet, the port can be adjusted in order to use a port-forwarding of an upstream security component, for instance.
The certificate used for access can be seen under SSL, and/or, with activated "Virtual hosting" (see GINA Domains GINA settings) under Secure GINA Host. |
|||
(optional) |
By default, this option is inactive. Provides access to the webmail subsystem (GINA portal) no longer directly but via the local SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway reverse proxy. All requests not specified for the webmail are thereby forwarded to the specified server address. This allows, for example, access to an internal OWA server (Outlook Web Access) with only one external IP address. Similarly, ActiveSync connections to the internal Microsoft Exchange server can be forwarded through the reverse proxy.
|
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
Enables the automatic query of public keys of the local users.
Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|
|
By default, this option is inactive. Activates the key server function of the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway. This makes the public keys, both S/MIME as well as OpenPGP, of the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway Users available to other systems, by means of LDAP via port 1389 and/or LDAPS via port 1636. For the secure communication via LDAPS, the certificate entered in the SSL will be used. A query is possible as follows: URI <Protocol>://<FQDN from Secure GINA Host Hostname> BindDN / BindPW is not required BaseDN is not required, although "dc=keyserver" works.
|
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
Enables the forwarding of log entries to a syslog server. Multiple servers can be entered and separated by a semicolon ";". By default, the port UDP/514 is used for transmitting the messages.
If necessary, the protocol as well as the target port can be optionally specified in the format [protocol]host[:port], for example tcp://192.168.10.60:1514.
|
Backups do not contain logs. In order to store them permanently and securely, it is recommended to set up the export of logs to an external system here.
|
Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|
SysLog server to which the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway is to send email, authentication and system logs. |
|
SysLog server to which the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway is to send logs of the activities from the administration interface. |
|
SysLog server to which the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway should send GINA protocols. |
|
By default, this option is inactive. Deactivates both the local creation of the mail log as well as the relevant statistics. |
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
Parameters |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Automatically delete log archives older than
This option is inactive by default and pre-set to 1095. Automatically deletes all Logs that are older than the set number of days. Automatically deleting the log archives •can help avoid setting up a "full" log partition. •ensures compliance with revision requirements regarding the retention of data.
Values from 1 to 3650 are accepted as input. The input of value ≥ 30 causes the default log rotation to be used. With this rotation, when the email log reaches a size of 30 MB (for the GINA log a size of 10 MB), the log is first archived and a new log file is started in each case. Since it is therefore not possible to delete exactly to the day, this procedure is primarily suitable to prevent the log partition from getting full. When a value ≤ 29 is set, on the other hand, the log rotates on a daily basis. This makes this procedure suitable for complying with revision specifications regarding the data retention period.
|
||
|
(new in 14.0.0) |
Select between File (maillog index files generated from the maillog files, default) or DB for the faster database approach, where maillog index files have been written to a database. In the DB case, it is possible to page through the log data.
|
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
Here, the corresponding settings are to be made only if direct access of the appliance to the Internet is impossible via SSH (see Use direct connection on port 22 outgoing (preferred)).
|
The settings made here are also used to obtain signature files of the Protection Pack, if applicable.
If the connection is established via a proxy, the port 22 connection is tunnelled via HTTPS Port 443. Access can then no longer be tested directly via the Rudimentary System Commands option "6) Port probe"). To this end, after calling up the option under Enter Server: enter the IP address 127.0.0.1 and under Enter Port: enter the number 23 . The reply Connection to 127.0.0.1 23 port [tcp/telnet] succeeded! should be shown if this was completed successfully. If not, the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway cannot establish the connection to the proxy server. In this case, the proxy settings would have to be checked again. If this check is successful but the connection is not established in the administration interface, it can be assumed that the request is stuck at the proxy.
|
Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|
Hostname or IP address of the proxy server via which the SSH communication is to be routed. |
|
Destination port of the proxy server, for example 8080 or 8081 |
|
|
(optional) |
User name for the login to the proxy server, if necessary. |
|
(optional) |
Password for the login to the proxy server. |
Default setting. This option must be activated if an SSH connection to the Internet is possible directly and without any detours, via a proxy server. |
|
This option must be activated to tunnel SSH connections through a generic SOCKS proxy. This option can be used if direct access to the Internet via SSH is regulated but the connection to the Internet is possible via a SOCKS proxy (version 4). |
|
This option must be activated to tunnel SSH connections through a generic SOCKS proxy. This option can be used if direct access to the Internet via SSH is regulated but the connection to the Internet is possible via a SOCKS proxy (version 5). |
|
This option must be enabled to tunnel SSH connections through an HTTP proxy. This option can be used if direct access to the Internet via the SSH is regulated, but the connection to the Internet is possible via an HTTP proxy. |
|
This option must be enabled to tunnel SSH connections through a Telnet proxy. This option can be used if direct access to the Internet via SSH is regulated, but the connection to the Internet is possible via a Telnet proxy. |
|
This option must be activated if an HTTP connection directly to the Internet is possible. The SSH connection then uses TCP port 80 (HTTP) instead of TCP 22 (SSH). |
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
 MPKI proxy settings (optional)
MPKI proxy settings (optional)
Here, the corresponding settings only have to be made if direct access of the corresponding MPKI interface to the issuing certification authority (CA) is impossible.
Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|
Hostname or IP address of the proxy server via which the communication with the certification authority via HTTPS port 443 is to be established. |
|
Destination port of the proxy server, for example 8080 or 8081. |
|
|
(optional) |
User name for the login to the proxy server, if necessary. |
|
(optional) |
Password for the login to the proxy server. |
Default setting. This option must be activated if the connection to the certification authority via the Internet is possible directly and without any detour by means of a proxy server via HTTPS port 443. |
|
This option must be enabled to tunnel connections to the certification authority through a generic SOCKS proxy. This option can be used if direct access to the Internet is regulated, but the Internet connection is possible via a SOCKS proxy (version 4). |
|
This option must be enabled to tunnel connections to the certification authority through a generic SOCKS proxy. This option can be used if direct access to the Internet is regulated, but the Internet connection is possible via a SOCKS proxy (version 5). |
|
This option must be enabled to tunnel connections to the certification authority through an HTTP proxy. This option can be used if direct access to the Internet is regulated, but the Internet connection is possible via an HTTP proxy. |
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
 OCSP / CRL check settings (optional)
OCSP / CRL check settings (optional)
This section can be used to activate the validity check of the certificate by means of revocation lists ("certificate revocation list" short "CRL") and/or the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP). For obtaining this information, access to the issuing certification authority (CA) is required in each case. If the appliance does not have direct access to the Internet, a connection via a proxy server can be configured in addition.
|
If the GINA certificate (see SSL) requires stapling (if needed, please also refer to https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Online_Certificate_Status_Protocol_stapling), the option Connect through HTTP proxy has to be active to guarantee that it functions correctly. When using this setting, possible entries under Proxy user and/or Proxy password are not transmitted to the entered Proxy server. |
Parameters |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
By default, this option is active. Activates the verification of certificates via OCSP/CRL.
|
|||
|
|
Hostname or IP address of the proxy server via which the HTTP/HTTPS communication to the CA is to be established. |
||
Destination port of the proxy server, for example 8080 or 8081 |
|||
|
(optional) |
User name for the login to the proxy server, if necessary. |
||
|
(optional) |
Password for the login to the proxy server. |
||
Default setting. This option must be activated if an HTTP/HTTPS connection directly to the internet is possible without a proxy server. |
|||
This option must be enabled to tunnel HTTP/HTTPS connections through a generic SOCKS proxy. This option can be used if direct access to the Internet is regulated via HTTP/HTTPS, but an Internet connection is possible via a SOCKS proxy (version 4). |
|||
This option must be enabled to tunnel HTTP/HTTPS connections through a generic SOCKS proxy. This option can be used if direct access to the Internet is regulated via HTTP/HTTPS, but an Internet connection is possible via a SOCKS proxy (version 5). |
|||
This option must be enabled to tunnel HTTP/HTTPS connections through an HTTP proxy. This option can be used if direct access via HTTP/HTTPS to the Internet is regulated, but an Internet connection is possible via an HTTP proxy. |
|
Certificates are not used only if they have been checked by means of OCSP or CRL and have been revoked. If a certificate cannot be checked using OCSP or CRL, it is still used. |
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|
Selection of the time zone applicable to the location of the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway. The switch between summer and winter time is carried out automatically. |
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
Parameters |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
With this setting, only the internal system time will be used. This can be set via Set date and time manually. There is no automatic synchronisation with other systems! |
|||
Default setting. With this setting, the time for virtual appliances would be compared to the host system if this is supported by the host system. With hardware systems, the corresponding sensor would be used for the comparison. |
|||
Default setting. The date and time will be synchronised with the time server given under Server via the NTP protocol, target port UDP 123.
|
|||
|
By default, it is pre-defined as pool.ntp.org. Hostname or IP address (IPv4 oder IPv6) of a time server. Several servers can be entered, separated by spaces. Where appropriate, the specification of a host name which is resolved into several time servers (pool) is advantageous for ensuring availability. If Internet time servers are used, local servers should be used whenever possible, for example de.pool.ntp.org instead of only pool.ntp.org. |
||
By default, this option is inactive. Periodically adjust the clock to avoid drift in virtual machines leads to a periodic adjustment of the time with the virtualisation host.
|
|||
If no NTP access is available, the current date and current time can be entered here manually. |
|||
|
Current date in the format: dd.mm.yyyy |
||
Current time in the format: hh:mm:ss |
|||
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
If no entry is made for snmp v1/2 read-only community nor for snmp v1/2 Read-write Community, SNMP v1/2 is deactivated.
For the SNMP v3 authentication SHA1 is needed, for encryption AES128 as algorithm.
Example:
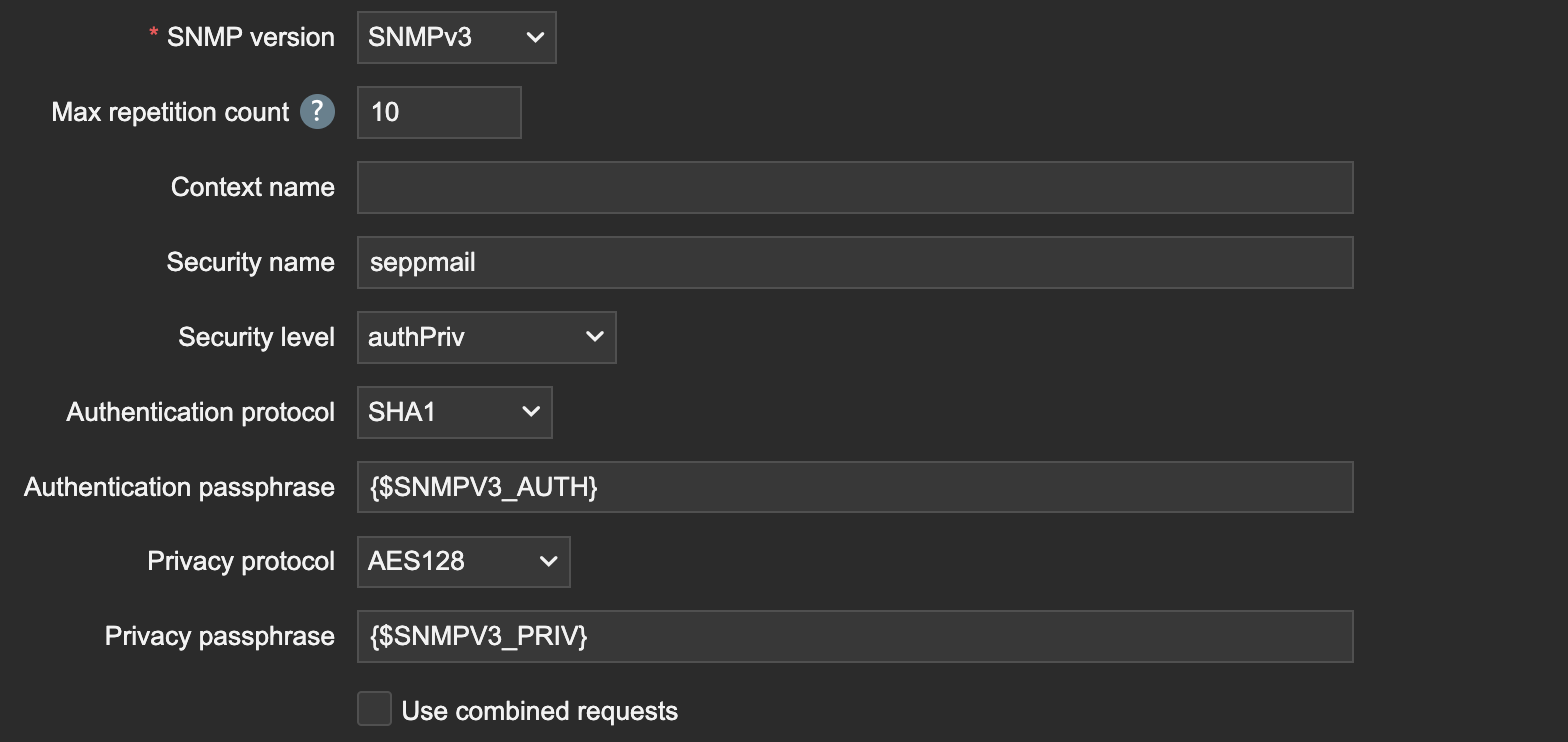
|
When monitoring partition utilisation, it should be noted that only those partitions are taken into account that are also listed under Home Disk statistics. All other partitions are read-only and up to 100% occupied. Monitoring these partitions would therefore lead to permanent messages. |
Parameters |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
By default, this option is inactive. Activates the SNMP Daemon on the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway. Thus, the SNMP protocol with tools, e.g. snmpwalk, can be used to call up information via the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway. |
|||
IP address - IPv4 or IPv6 - to which the SNMP monitoring connects. Generally, this is the IP address of the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway. Entering several addresses is not possible. |
|||
Password for read-only access to the SNMP data. |
|||
Password for read-write access to the SNMP data. |
|||
User name for SNMP v3 access |
|||
Password (user and privacy) for the SNMP v3 access. This must contain at least eight characters. |
|||
Via the button, the management information bases (MIB) of the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway can be downloaded as a ZIP file. In addition, the following OIDs are available for monitoring further functions: .1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.1.0 = INTEGER: 10
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.2.1.3.11.109.97.105.108.115.80.103.112.68.101.99.0 = STRING: mailsPgpDec
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.2.1.3.11.109.97.105.108.115.80.103.112.69.110.99.0 = STRING: mailsPgpEnc
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.2.1.3.13.109.97.105.108.115.83.109.105.109.101.68.101.99.0 = STRING: mailsSmimeDec
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.2.1.3.13.109.97.105.108.115.83.109.105.109.101.69.110.99.0 = STRING: mailsSmimeEnc
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.2.1.3.14.109.97.105.108.115.68.111.109.97.105.110.68.101.99.0 = STRING: mailsDomainDec
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.2.1.3.14.109.97.105.108.115.68.111.109.97.105.110.69.110.99.0 = STRING: mailsDomainEnc
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.2.1.3.14.109.97.105.108.115.80.114.111.99.101.115.115.101.100.0 = STRING: mailsProcessed .1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.3.1.1.18.109.97.105.108.101.117.101.65.99.116.105.118.101.0 = STRING: mailsInQueueActive .1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.3.1.1.20.109.97.105.108.101.117.101.68.101.102.101.114.114.101.100.0 = STRING: mailsInQueueDeferred
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.2.1.3.20.109.97.105.108.101.117.101.73.110.99.111.109.105.110.103.0 = STRING: mailsInQueueIncoming
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.3.1.1.11.109.97.105.108.115.80.103.112.68.101.99.0 = STRING: 17
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.3.1.1.11.109.97.105.108.115.80.103.112.69.110.99.0 = STRING: 14
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.3.1.1.13.109.97.105.108.115.83.109.105.109.101.68.101.99.0 = STRING: 0
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.3.1.1.13.109.97.105.108.115.83.109.105.109.101.69.110.99.0 = STRING: 0
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.3.1.1.14.109.97.105.108.115.68.111.109.97.105.110.68.101.99.0 = STRING: 0
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.3.1.1.14.109.97.105.108.115.68.111.109.97.105.110.69.110.99.0 = STRING: 2
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.3.1.1.14.109.97.105.108.115.80.114.111.99.101.115.115.101.100.0 = STRING: 6409 .1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.2.1.3.18.109.97.105.108.101.117.101.65.99.116.105.118.101.0 = STRING: 0 .1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.2.1.3.20.109.97.105.108.101.117.101.68.101.102.101.114.114.101.100.0 = STRING: 0
.1.3.6.1.4.1.8072.1.3.2.3.1.1.20.109.97.105.108.101.117.101.73.110.99.111.109.105.110.103.0 = STRING: 0
|
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
In this section, the NRPE (Nagios Remote Plugin Executor) for monitoring the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway via Nagios is configured.
|
When monitoring partition utilisation, it should be noted that only those partitions are taken into account that are also listed under Home Disk statistics. All other partitions are read-only and up to 100% occupied. Monitoring these partitions would therefore lead to permanent messages. |
Parameters |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
By default, this option is inactive. Activates the Nagios Daemon on the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway for monitoring the system. |
|||
Input of the IP address - IPv4 or IPv6 - to which the NRPE client should connect. Entering several addresses is not possible. If no input is made, the daemon listens on all existing interfaces ( IP addresses). (corresponds to the parameter "server_address=" in the NRPE configuration file "nrpe.cfg") |
|||
|
(above 1024) |
Port on which the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway expects NRPE queries. By default, this is port 5666. If a port other than the default port is used, it is to be ensured that it is not used by another service and is higher than 1024. If an already occupied port is accidentally used, a watchdog would report that the service is no longer running. (corresponds to the parameter "server_port=" in the NRPE configuration file "nrpe.cfg") |
||
|
hosts/networks |
Entry of the IP addresses or subnetworks authorised for the query. The entry is made in the format 192.168.0.0/24 or 2a00::/112. Several entries can be separated by a comma. If no entry is made, requests are accepted from any address. (corresponds to the parameter "allowed_hosts=" in the NRPE configuration file "nrpe.cfg") |
||
By activating the option Allow remote command arguments, the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway also accepts the arguments transmitted with the queries of the NRPE clients. (corresponds to the parameter "dont_blame_nrpe=1" in the NRPE configuration file "nrpe.cfg")
|
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
The following Nagios plugins are integrated into the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway for use with variable parameters. Using variable parameters is made possible by activating the option Allow remote command arguments. The parameters listed for the command are to be transferred mandatorily.
Command |
Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|---|
check_disk |
-w $ARG1$ |
Threshold value (in %) for free disk space below which the message "warning" is issued (for example "20%"). |
-c $ARG2$ |
Threshold value (in %) for free disk space below which the message "critical" is issued (for example "10%"). |
|
-p $ARG3$ |
Path of the file system to be checked (for example "/var/log"). |
|
check_swap |
-w $ARG1$ |
Threshold value (in %) for free swap space below which the message "warning" is issued (for example "60%"). |
-c $ARG2$ |
Threshold value (in %) for free swap space below which the message "critical" is issued (for example "40%"). |
|
check_mailq |
-w $ARG1$ |
Threshold value for the number of emails in the queue upon the exceedance of which the message "warning" is issued (for example "1000"). |
-c $ARG2$ |
Threshold value for the number of emails in the queue upon the exceedance of which the message "critical" is issued (for example "1500"). |
|
check_load |
-w $ARG1$ |
Threshold value for the system utilisation [avg1,avg5,avg15], upon the exceedance of which the message "warning" is issued (for example "15,20,20"). |
-c $ARG2$ |
Threshold value for the system utilisation [avg1,avg5,avg15], upon the exceedance of which the message "critical" is issued (for example "20,25,35"). |
|
check_procs |
-w $ARG1$ |
Threshold value for the number of processes upon the exceedance of which the message "warning" is issued (for example "5"). |
-c $ARG2$ |
Threshold value for the number of processes upon the exceedance of which the message "critical" is issued (for example "10"). |
|
-s $ARG3$ |
Indication of the processes to be monitored (e.g. "Z" for zombie processes). |
|
check_smtp (new in 14.1.4) |
-H $ARG1$ |
Indication of the IP address to which the SMTP connection is to be checked (for example localhost). "localhost"). |
-p $ARG2$ |
Indication of the port to be checked (for example "25"). |
|
check_tcp |
-H $ARG1$ |
Indication of the IP address to which the TCP connection is to be checked (for example localhost). "localhost"). |
-p $ARG2$ |
Indication of the port to be checked (for example "25"). |
|
check_telnet |
-H $ARG1$ |
Indication of the IP address to which the Telnet connection is to be checked (for example "localhost"). |
-P $ARG2$ |
Indication of the port to be checked (for example "25"). |
|
-M $ARG3$ |
Indication of the banner string to be checked (for example "ESMTP"). |
Table: Plugins with variable parameters
The plugins which continue to be integrated may also be used if the option Allow remote command arguments is deactivated. These are then to be used without parameters.
Command |
Specification Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|---|
check_disk_tmp_static |
-w 10% |
See table Plugins with variable parameters Command check_disk |
-c 5% |
||
-p /tmp |
||
check_disk_db_static |
-w 25% |
|
-c 10% |
||
-p /var/ldap.ENCRYPTED |
||
check_disk_log_static |
-w 25% |
|
-c 10% |
||
-p /var/log |
||
check_disk_mq_static |
-w 40% |
|
-c 10% |
||
-p /var/mailqueue |
||
check_mailq_static |
-w 100 |
See table Plugins with variable parameters Command check_mailq |
-c 250 |
||
-M postfix |
||
check_telnet_static |
-H localhost |
See table Plugins with variable parameters Command check_telnet |
-P 25 |
||
-M ESMTP |
||
check_zombie_procs_static |
-w 5 |
See table Plugins with variable parameters Command check_procs |
-c 10 |
||
-s Z |
||
check_load_static |
-w 5,10,15 |
See table Plugins with variable parameters Command check_load |
-c 20,25,30 |
Table: Plugins with static parameters
(new in 13.0.0)
In this section, the configuration of the Zabbix agent is carried out, which is responsible for monitoring the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway via the Zabbix Monitoring Tool.
Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|
By default, this option is inactive. Activates the Zabbix Agent. With this, the basic default options of Zabbix (see also https://www.zabbix.com) are available. Further options can be defined under Options. |
|
Input of the IP Addresses of the interface on which the agent is to accept requests from the Zabbix monitoring tool. Multiple entry of IP addresses is possible, so that both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses can be used in parallel. As separator, use a comma ",". |
|
Input of the IP port on which the agent is to accept requests from the Zabbix monitoring tool on the Listen address set above. |
|
Input of the IP address(es), or IP network(s) in CIDR notation, from which the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway is to accept requests from Zabbix. |
|
By default, additional options for monitoring the postfix are already predefined: UserParameter=postfix.holdtotal,sudo /usr/local/sepp/scripts/zbx_qshape.pl hold T UserParameter=postfix.hold5,sudo /usr/local/sepp/scripts/zbx_qshape.pl hold 5 UserParameter=postfix.hold10,sudo /usr/local/sepp/scripts/zbx_qshape.pl hold 10 UserParameter=postfix.hold20,sudo /usr/local/sepp/scripts/zbx_qshape.pl hold 20 UserParameter=postfix.deferredtotal,sudo /usr/local/sepp/scripts/zbx_qshape.pl deferred T UserParameter=postfix.deferred5,sudo /usr/local/sepp/scripts/zbx_qshape.pl deferred 5 UserParameter=postfix.deferred10,sudo /usr/local/sepp/scripts/zbx_qshape.pl deferred 10 UserParameter=postfix.deferred20,sudo /usr/local/sepp/scripts/zbx_qshape.pl deferred 20 UserParameter=postfix.activetotal,sudo /usr/local/sepp/scripts/zbx_qshape.pl active T UserParameter=postfix.active5,sudo /usr/local/sepp/scripts/zbx_qshape.pl active 5 UserParameter=postfix.active10,sudo /usr/local/sepp/scripts/zbx_qshape.pl active 10 UserParameter=postfix.active20,sudo /usr/local/sepp/scripts/zbx_qshape.pl active 2
These can be extended, if necessary. If the options are to remain empty, a blank " " is to be entered. If the input field remains empty, the default values are restored. |
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
 Virtualisation tools (Detected Environment: <Virtualiser>) (optional)
Virtualisation tools (Detected Environment: <Virtualiser>) (optional)
(changed in 13.0.0)
This section is only available on virtual appliances.
The respective options are active depending on the virtualisation host used (see note in the section name). All other options are greyed out.
Parameters |
Description |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
By default, this option is active. An OS kernel with integrated VMware tools is used. These tools may cause problems in a few constellations under ESX as well as with some backup tools which use "quiescing". For this reason, they can be deactivated. Any change made here will only become active once the SEPPmail Secure E-Mail Gateway has been restarted. |
|||
|
By default, this option is inactive. Activates the Microsoft Azure Linux Agent. The monitoring functions of the Azure Fabric Controller are thus also available. It is not possible to make any settings in this way.
|
|||
|
(removed in 13.0.4) No longer necessary, the normal DHCP-based network settings are used.
|
|||
|
Disable vioscsi driver (Check if startup hangs on vioscsi, change disk controller to IDE first) |
By default, this option is inactive. If start problems happen with "vioscsi", proceed as follows: in the virtualisation environment, first the network controller setting "vioscsi" needs to be changed to "IDE" and after restart the option needs to be activated. |
||
The changes made are saved via the Save button.
If several sections have been edited, via the button Save and apply all all can be saved globally.














 , the
, the  a new
a new 